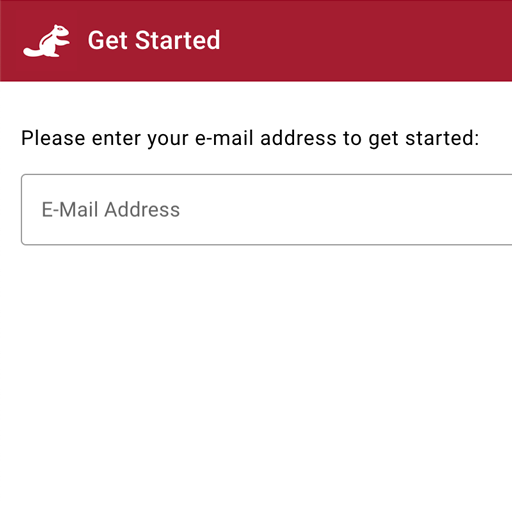
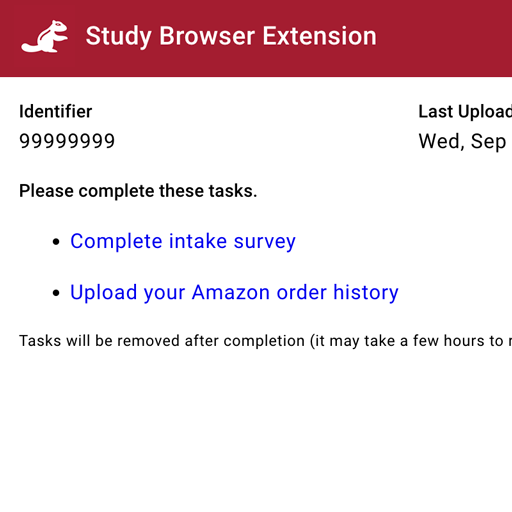
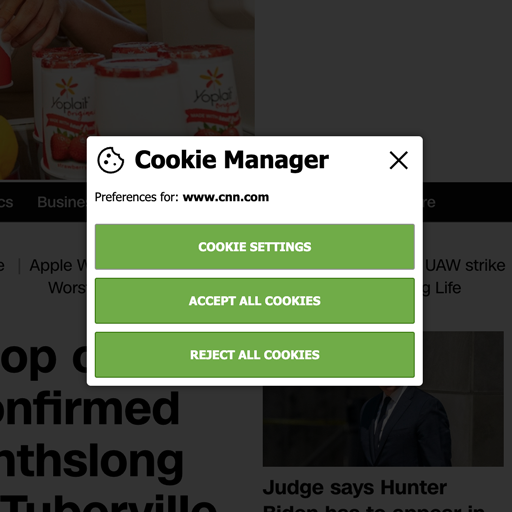
Webmunk 2 is a web browser extension and data collection platform for conducting observational and experimental research studies on the Internet. Webmunk 2 is open-source and available to all interested researchers. You can access the code and documentation in the Webmunk 2 repository.
Note that Webmunk 2 replaces the original Webmunk, which was released in 2024. Webmunk 2 is a substantial improvement over the original Webmunk. It is easier to use, cheaper, and more powerful than the original Webmunk. It also uses a standard stack on the back-end (Jitsu, Firebase, and BigQuery), making it more accessible to researchers and software developers.
The primary creators of Webmunk are Chiara Farronato (Harvard Business School), Andrey Fradkin (Boston University), Audacious Software, and Unibrix. Please contact Professors Farronato or Fradkin to discuss any research related aspects of Webmunk.
Webmunk is a research project supported by the Fradkin Foundation and the President & Fellows of Harvard College.
Functionalities
Tracking a user’s experience:
- Web browsing history.
- Website content.
- Browser settings.
- User interactions with websites (e.g. scrolling).
- Cookies.
Modification of user experience:
- Changing the look and feel of a website.
- Inserting new content and new interactions into the website.
- Removing and setting cookies.
- Acting as a user proxy, by for example filling in forms and selecting options.
- Reminding users to fill out surveys and conduct certain actions.
Details
The browser extension component of Webmunk 2 is designed for the Chrome and Edge browsers. The extension can modify the content of web pages in real time and collect data as users browse the Internet. By keeping track of (anonymized) user identities, the extension can implement different web page manipulations across users or over time, which enables researchers to assign different experimental interventions that they may want to compare. The extension uses various techniques to engage study participants in specific tasks beyond their regular browsing activity, such as completing surveys or visiting designated websites.
The cloud component of Webmunk 2 works as follows. First, events such as page visits and clicks are passed to Jitsu which receives and routes data. Second, Firebase is used to validate events, applying study rules, managing enrollment, and preparing data for storage. Third, the data is stored in BigQuery on the Google Cloud Platform, for the purposes for running queries.
Webmunk 2 is open-source and designed to be easily extended through the use of modules. Modules are self-contained and re-usable components that work with Webmunk. In our projects, we've designed modules for identifying products on Amazon and for retrieving users' Amazon order histories. Modules are particularly useful for implementing manipulation and tracking that is particular to a web domain.